Electrospinning is more commonly known for its use as a manufacturing process in the production of nanofiber materials, typically for fabrics in clothing and air filtration.
However, with dedicated research, the versatility of the process and the materials used are showing an increased benefit across the food industry as well. By using the process to electrospin biopolymers, the process can be used in the encapsulation of food ingredients, enzymes and other things.
Usage can ensure that the consumables can be kept preserved and fresh until consumed, and now research has even begun to see if the process can be used to add different textures to the food itself, or potentially even artificial food replacements created at a molecular level.
Electrospinning applications of biomaterials extended to food
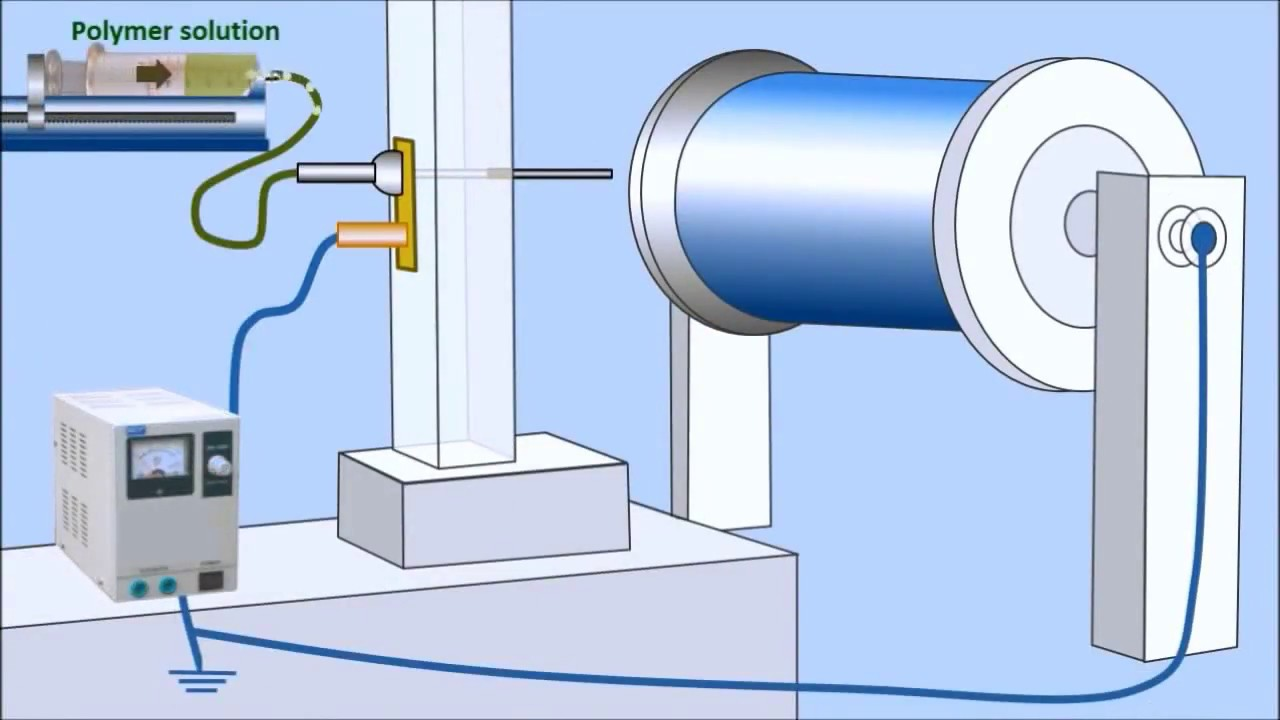
Electrospinning is the process by which polymers and melts are electrically charged in order to form a stream of particles that can be whipped into fibers, and the fibers used in the production of nanomaterials.
With the advent of the electrospinning machine, the ability to use the process on a wide variety of materials became very much apparent. Using biomaterials to produce the polymers very quickly found use for medicinal purposes, and natural polymers such as collagen helped with this.
Research then turned to electrospinning of soy protein and whey protein, although the physics has proved challenging and other polymers needed to be added in order to produce good nanofibers.
Of course, one of the challenges was to eliminate potentially harmful solvents present in some electrospinning procedures, and so water soluble polymers are often used. Some experiments have been carried out in the production of chocolate, using salt, sugar, milk and cocoa, but the best application has been in the creation of ‘sugar syrup’ fibers.
Packaging of food allows for better preservation and shelf life
With global supply chains now in place for food, the difficulties are preservation during transit means that a longer shelf life is now very important for food being transported globally.
Alongside this food safety is of the utmost importance, and import of food stuffs expected to meet very high international standards. Nanotechnology addresses these needs head on, by enabling the creation of new food and beverage packaging. With the right packaging the food industry is seeing improved taste, colour, flavour, texture and consistency of food.
Not only this when it comes to the longevity of health supplements, nanofiber packaging is ensuring that the nutritional value of such supplements does not degrade over time.
Better release of nutrients into the body
Where electrospinning is showing the most promise in the food industry, is through the encapsulation of health supplements and medicines.
Not only is the product preserved and protected during production, but the addition of antibacterial properties puts this new process steps ahead of current encapsulation methods. Protection of the nutrients continues after consumption, protecting product as it passes through the digestive system from harsher conditions such as stomach acid to ensure the nutrients are released at the right moment into the body and blood stream. It makes the absorption of nutrients all the more efficient and beneficial.
That said the application of electrospinning in the food industry, and also its potential for producing artificial food replacement is still very much in its infancy. But with electrospinning machines being more commercial available, the set up of research labs cheap by comparison and the ease at which someone with a basic knowledge of polymers and electrostatics can learn how to do it, companies are investing in the academic research needed to find out what the next big impact electrospinning will have on the food industry will be.
Join the discussion on this topic with The Tech Block by visiting our contact page.